Introduction
New technologies and processes have facilitated businesses’ international expansion, and these days there are more and more businesses looking to build their international presence due to the impact this could have on their growth.
There are multiple factors that could influence this decision, whether this is because your local market is saturated with competitors, or a new opportunity to take your brand globally has appeared. This guide will provide you with some useful SEO tips to take into consideration when going global.
Guide Contents
What’s international SEO?
International SEO refers to the process of growing your business’ organic presence across different countries.
Once a business decides to go international, one of the most important considerations is to ensure the website is set to be competitive in such markets, as this will help succeed in the expansion.
Why is international SEO important?
With the business’ website being one of the most crucial touchpoints, having an optimised website with localised content could help meet users’ expectations.
Although going global has some challenges, when international SEO is done right, it presents multiple benefits including:
Access a wider audience
Launching in new countries means that you will get access to a new audience.
Drive organic traffic & revenue
This goes hand in hand with reaching a new audience. Following the best practices would help maximise your performance and drive more sessions and revenue to your site.
Provide a good user experience
Users who have a positive experience with a brand are more likely to become repeated customers. Additionally, providing a good user experience is one of the many guidance that search engines require to increase your ranking potential.
Build brand awareness
Helping to position your brand globally and consolidate in the new regions.
How to set your website to go global?
Once we’ve learned what international SEO is and why it’s important, this section will cover some of the top tips that would help you be successful when taking your brand globally.
Decide which countries to target
When it comes to deciding what countries to target first, we’d recommend analysing your current online performance as this could help bring some light to what regions to prioritise.
There are different tools that could be used to identify where your current traffic is coming from, with one of the most reliable ones being the countries search results report from Google Search Console.
Ahrefs is another useful tool that would help see which countries are contributing to the total organic traffic to your site.
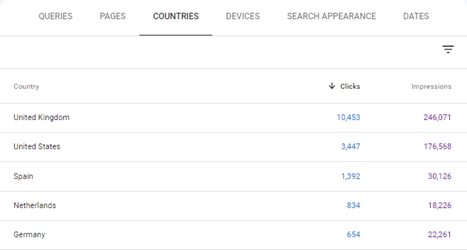
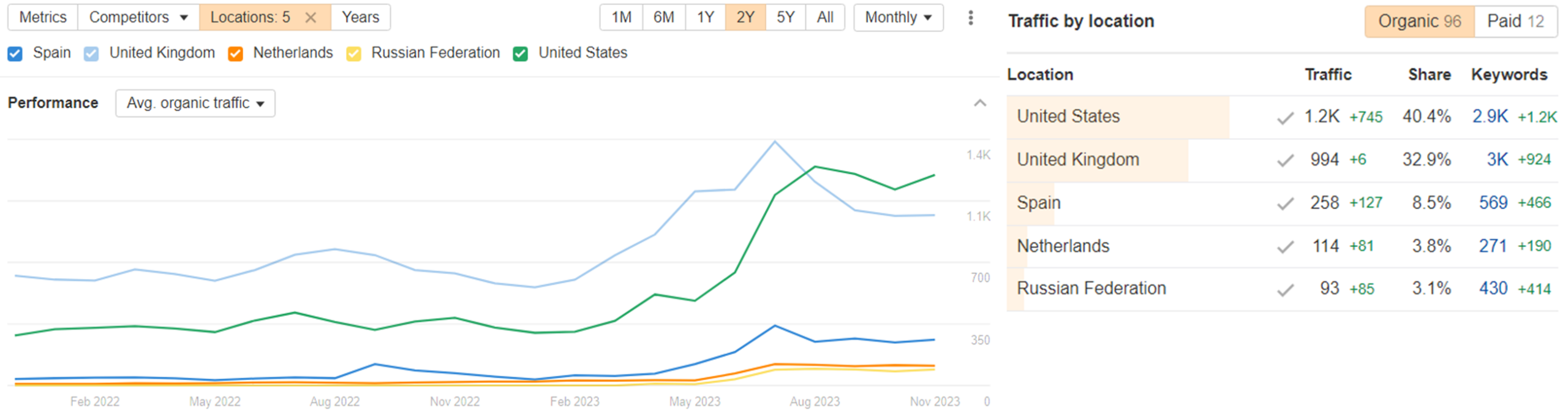
While these reports are useful, there are other things to consider when making the decision, such as the potential search demand for your products/services, the competitiveness in the market or the business capacity to fulfil orders from such regions, to list some of them.
We’d advise carrying out an initial keyword research to understand demand levels, as well as trends in the market.
Some of our favourite keyword research tools include:
- SEMrush or Ahrefs: To carry out a competitor analysis and identify similar search terms.
- Google trends: To get more insights at a city/regional level.
- Keyword planner: To analyse search demand over time and identify seasonality periods.
Once you are set on which countries to launch, it’s time to talk about how to launch on those regions with your website.
Decide the URL structure
Reaching new countries could be challenging but using the right locale-specific URLs could help you on the way.
We’d suggest following Google’s recommendations on URL structures, which include:
Country-specific domain:
This is one of the most popular options as it sends clear geotargeting signals and there’s a clear separation of sites. This approach is also useful when the server location isn’t an issue. Some examples:
- https://www.amazon.co.uk/
- https://www.amazon.es/
- https://www.amazon.it/
The downside of this approach is that it obviously requires more infrastructure and it’s expensive. Additionally, a new domain would be needed to target different countries.
Subdomain with a generic top-level domain (gTLD):
Another option is using subdomains, as it’s easy to set up and it also offers a clear separation of sites.
- https://us.speedo.com/
- https://de.speedo.com/
- https://it.speedo.com/
The con of this structure is that users might not recognise the geotargeting from the URL itself.
Subdirectory with gTLD
Using subdirectories is probably the easiest way to launch internationally, as they require low maintenance. However, the separation of the sites is harder. They only allow a single server location and users may not reorganise the geotargeting from the URL alone.
- https://www.apple.com/uk/
- https://www.apple.com/es/
- https://www.apple.com/it/
There are cons and pros of each of the above, and therefore the decision on which one to use would depend on your business goals and resources.
International optimisation
Once we know what countries to target and their languages, and a decision on the URL structure has been made, it’s time to ensure the website is fully optimised for each region.
It’s recommended to have as many unique and localised signals as possible. Some of the key optimisation elements include:
Translations
All content on the new sites would need to be translated into the local language, not only to offer a good user experience and reduce bounce rate but also to perform well organically.
Even if your expansion is to other English-speaking countries for example, it’s still recommended to optimise your content for the new region, as they may use different expressions/terms.
Currency and pricing
The right pricing and currency would need to be displayed to ensure users can place an order and complete a transaction.
It’s also important to know the different ways other countries express numerical values, to help with this, we’ve written a useful guide on how to translate and localise values.
Additionally, an understanding of the foreign regulations around pricing and promotions would be key to running a successful online business.
Sizing and fit
To minimise returns, it’s recommended to have the local size and fitting details.
Trust signals
Delivery and returns details should be localised, as well as the contact details and any other trust signals on the website.
Technical international SEO
There are also some technical SEO elements that you would need to implement when launching your website in multiple countries and languages:
Hreflang implementation
Hreflang tags indicate to search engines the language used on each URL, to serve the right results to users in that language.
It’s recommended to use hreflang tags to help search engines understand the relationship between pages that have similar content in different languages or the same language but with different spelling e.g., British English vs American English.
It’s also important to understand that hreflangs are a signal, not a directive and so it’s recommended to use them in conjunction with the other localisations signals mentioned earlier such as pricing or delivery details.
If you would like to learn more about hreflang implementation, check out our latest hreflang tags guide for beginners.
Page speed optimisation
Providing a good user experience is key to reducing bounce rate and driving conversions and page load speed is something that will contribute to it.
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is recommended when operating in multiple locations. A CDN is a group of servers distributed geographically which help speed up the delivery of your website content closer to the users.
CDNs will not only help improve the website load times, but they also help reduce the bandwidth cost and improve security against malicious attacks amongst other benefits.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Introduction
If you are planning on taking your online business international and target different countries and languages, you may have heard about hreflang tags, which is one of the most complex elements of SEO.
There are other technical best practices to follow for multilingual/multi-regional websites, but in this guide, we are going to offer a complete hreflang tags guide for beginners.
Guide Contents
You may be wondering what the benefit of implementing these tags is if it’s not rankings, but their main objective goes beyond ranking higher on Google.
When hreflangs are implemented correctly, they could help reduce bounce rate and increase user engagement as the relevant version of a page is served to users.
For example, a business operating in the UK and in Spain with two different versions of a page would want to ensure that Spanish speakers are served the translated version of a page.
Additionally, when operating in countries that speak the same language e.g. United States, Australia or the United Kingdom, hreflang tags could help prevent these pages from competing against each other in SERPs.
When it comes to the implementation of hreflang tags, it’s worth mentioning that there are 3 different ways to do this, which are:
- Using on-page markup
- HTTP header
- XML Sitemap
Google’s documentation indicates that all three methods are valid and that there’s no preferred way to implement these tags. However, it’s recommended to only use one of the above methods.
The below guidelines apply to all methods:
- Each language version of the page must list itself and all the other language versions. This is very important, because if there isn’t a return tag, these will be ignored.
- A full URL must be used, not just the URL string.
- Alternate URLs don’t need to be under the same domain.
- It’s recommended to use the “x-default” value for any unmatched language or country.
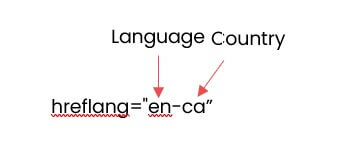
- Use the standardised nomenclature for language and country codes. Google uses the ISO 639-1 format for language codes, and the ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 format to represent the country.
Creating and mapping hreflang tags could be a daunting task, however, luckily for us, there are loads of tools in the market that could help with this.
We need to differentiate between tools that help generate such tags and those that can check the implementation of the annotations to ensure everything is working as intended.
Hreflang tag generators
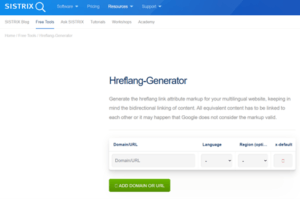
Sistrix
Apart from being a powerful tool to have a view on websites’ visibility, keywords and competitor analysis, one of the free tools that they have is a hreflang tag generation tool, which is very intuitive and easy to use.
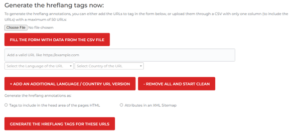
Aleyda Solis
Aleyda Solis have developed a tool that allows generating annotations to up to 50 URLs in bulk using a CSV file.
After adding the URLs, you’d just need to select the language and country, as well as the method you will use to implement the tags, via HTML or XML sitemap.
Hreflang tag checkers
Ahrefs
Apart from being one of our favourite keyword research tools, it’s also a great tool to check and monitor the hreflang tags implementation.
Ahrefs’ site audit tool will flag issues such as pages missing tags, invalid annotations and many more. This report can be found under the ‘localization’ section.
There are other site crawlers such as Screaming Frog, which are also useful for monitoring your website’s international setup.
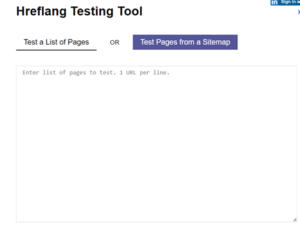
Hreflang.org
Hreflang.org is another easy-to-use testing tool that allows you to check the implementation of hreflang tags in bulk, as well as those that have been added via the XML sitemap.
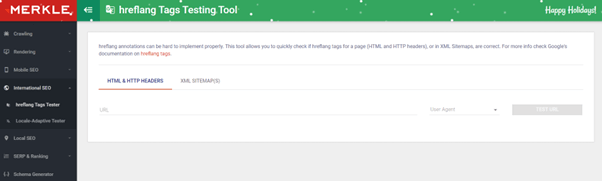
Merkle
Merkle offer a wide range of tools, from robots.txt testers to sitemap generator. In this case, we are going to talk about the hreflang tags tester, which is a powerful tool to check hreflang annotations regardless the method used to implement them, HTML & HTTP headers, as well as XML sitemap checker.
In conclusion
Although hreflang annotations are a very complex element of SEO, the correct implementation will help boost your SEO performance when targeting different languages and regions. Once you are set to go global, you’d need to decide which of the three implementation methods is best suited for your website, as this will guide you on which tool to use to generate and check their implementation.
If you are looking for an international SEO agency to help with your upcoming expansion plan, please don’t hesitate to get in touch. Alternatively, you can find out more about our international SEO services online.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Introduction
HTML headings? You’ve likely heard of them but what actually are they, what is their purpose and how do you write them?
In traditional print content, headings are phrases at the beginning of a section that explain what it’s about. Well, it’s much the same when it comes to headings on the World Wide Web, too. Correct use of HTML headings on a web page provides structure and a quick run-down of what a webpage is about, helping both search engine bots and humans understand your content.
So, if you want to improve your SEO efforts, HTML headings are a good place to start. But getting your head around even the most basic HTML can be difficult. Luckily for you, we’ve put together this handy beginner’s guide to HTML headings. In this guide, we’ll learn what HTML headings are, how they benefit SEO and how to write HTML heading tags correctly.
Points we’ll touch on:
What is HTML?
HTML, or Hypertext Markup Language, is the basic building block of most web pages – a system for telling browsers how to structure content. For example, the language can be used to specify which part of a page is the title, which is a heading, a list, an image and so on. It can also be used to hyperlink a word, embed an image, bold a font and so much more.
It is one of three essential components that web designers use to create websites, alongside Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and Javascript (JS). In web design, HTML acts as the simple base upon which to build CSS and JS. While CSS allows you to customise your web page with colour, fonts, styling and layouts, JS allows you to add dynamic functionality like pop-ups and sliders.
What are HTML headings?
Now for the good stuff…
HTML headings are titles or subtitles that you want to display on a webpage. These heading tags are used to differentiate the headings (<h1>) and sub-headings (<h2>-<h6>) of a page from the rest of the content.
HTML defines six levels of headings, including H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6. The most important heading is the H1, while the least important is the H6. The heading tags from H1 to H6 form a top-down hierarchy, which means that if you skip any of the tags, the structure will be broken. This is bad news for SEO.
Improving readability
Adding headings and subheadings to a page divides the content into easy-to-scan blocks that both readers and bots can consume.
Like headings in print content, heading tags are used to title or introduce the content below them. As already mentioned, HTML tags follow a hierarchy, from <h1> to <h6>:
- H1 tags – used to denote the most important text, such as the overall topic or title
- H2 and H3 tags – usually used as sub-headings
- H4, H5 and H6 tags – provide further structure within those subsections
HTML heading tags are incredibly useful for both users and search engines. For users, headings give them a preview of the content they’re about to read. For search engines, such as Google, a heading is a strong signal that tells them the topic of a specific section.
So, ultimately, heading tags are important for SEO because they help Google understand your content, while also making your web pages more user-friendly.
Highlight relevant keywords
Search engine bots see the text used within HTML heading tags as more valuable compared with the rest of the text on the page. Therefore, search engines weigh the words included in the heading tags more highly when they’re trying to determine a page’s relevancy to users’ search queries. In fact, a page’s H1 tag is one of the most impactful places you can use a keyword.
For example, if the main keyword you want to target is “HTML headings”, you would use that in your H1 tags. Then, you would include any semantically related keywords throughout the rest of your content, including your subheadings.
Like headings in print content, heading tags are used to title or introduce the content below them. As already mentioned, HTML tags follow a hierarchy, from <h1> to <h6>:
- H1 tags – used to denote the most important text, such as the overall topic or title
- H2 and H3 tags – usually used as sub-headings
- H4, H5 and H6 tags – provide further structure within those subsections
HTML heading tags are incredibly useful for both users and search engines. For users, headings give them a preview of the content they’re about to read. For search engines, such as Google, a heading is a strong signal that tells them the topic of a specific section.
So, ultimately, heading tags are important for SEO because they help Google understand your content, while also making your web pages more user-friendly.
What are HTML headings?
What is an H1 tag?
So, as mentioned above, H1 tags are the most important HTML heading. Why? Essentially, it acts as the page title. The H1 tag is a critical ranking factor for search engines, being considered by bots to determine what a page is all about.
Also, given that H1-tagged content tends to appear larger on a webpage, the H1 tag is typically the very first page element seen by readers, making it a determiner of whether they keep on reading or go back to the search results page (SERP).
What is the difference between a heading and a subheading?
While a heading acts as the title of a piece of content, a subheading acts as an extension of that heading.
The purpose of the heading, or H1 tag, is to grab the attention of both humans and search engine bots. Humans read a heading to determine whether the content is relevant to them, while bots read a heading to find out whether it is relevant to any search queries.
By contrast, the subheading is placed right below the heading and drives the reader to continue reading through the rest of the content.
SEO H1 tags best practices
Considering that H1 tags are clearly so important, it’s crucial that you know how to properly optimise them for SEO. To do so, follow our SEO H1 tags best practices below:
- Use H1 tags for page titles
- Use title case for H1s
- Match H1s to title tags
- Only use one H1 tag per page
- Use an H1 tag on every important page
- Keep H1 tags short
- Include your target keyword
- Make H1 tags compelling
SEO H1 tags best practices
Considering that H1 tags are clearly so important, it’s crucial that you know how to properly optimise them for SEO. To do so, follow our SEO H1 tags best practices below:
- Use H1 tags for page titles
- Use title case for H1s
- Match H1s to title tags
- Only use one H1 tag per page
- Use an H1 tag on every important page
- Keep H1 tags short
- Include your target keyword
- Make H1 tags compelling
What are H2 tags?
Whereas your H1 tag is used for your page’s main heading, your key points are wrapped up in subheadings known as H2s. In other words, your <h2> tag defines the second-level heading on your webpage.
What are H3 tags?
However, subheadings don’t just stop at H2s. Any sub-points below your <h2> tags should use <h3> heading tags, while sub-points below H3s should use the <h4> heading tag, and so on.
This sequence can continue all the way to <h6> tags, which are the least important in the heading tag hierarchy.
How to write HTML headings
Overall, writing HTML headings is about organising your content in a way that makes it easier for readers to scan and understand. Therefore, headings should be used hierarchically, starting with your H1 tag and working your way down to H2, H3 and beyond.
If you’re just writing a short piece of content, you might only have a single H1 tag and a couple of H2 tags. But for longer, more complex content, you might require headings through to H6 to make your content more readable.
When structuring your headings, focus on breaking down the topic into clear, logical sections – don’t just create headings for the purpose of SEO. Your H1 should introduce the topic, while your H2 subheadings should break that topic down into key sections. Any following headings should then add extra detail.
The different HTML heading levels should be written as follows:

This code would result in:

For example, if you were writing a content piece about the benefits of owning a dog, your heading structure might look a little like this:

Takeaways
So, what do you need to take away from our beginner’s guide to HTML headings?
First, HTML headings are still an important ranking factor for SEO. So, using them properly will help improve the organic ranking performance of your website.
Finally, when writing HTML headings, structure them in a logical way that will help both readers and search engine bots make sense of your content.
Find out more about our SEO services and get in touch today. Or, to learn more about digital marketing, visit our blog.
Second, HTML heading tags also improve user experience by making your content easier to read and understand.
Third, HTML heading tags should be used hierarchically, with H1 at the highest level and H6 at the lowest. H1 tags are most important and should include your target keyword.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
If you’ve ever Googled anything in your entire life, odds are you’ve seen a featured snippet.
You know what we’re talking about, right?
Those little boxes of info that appear at the top of a search page usually include some of the information you’re looking for.
Featured snippets are a small but major brick that helps support the numerous building blocks that go into making the digital and organic marketing world function, which makes it very important to learn their benefits so you can start making use of them as well.
However, while featured snippets might seem like a simple concept to grasp, as you’ll soon see, there’s far more that goes into learning how to optimise for featured snippets than just cobbling together a bunch of bullet points and slapping them in a list.
That’s why we’ve created this little guide, so you can learn what a snippet is, what kind of role they play in search engine rankings, and how best to optimise your content so you can grab yourself a few in the future.
Points we’ll touch on:
With introductions out of the way, let’s get straight down to business and go through everything that goes into making featured snippets work, starting with the obvious question, what is a featured snippet?
What is a featured snippet
The eagle-eyed readers amongst you might already want to point out that we’ve already given a vague explanation for what a featured snippet is, but let’s touch on it in slightly more detail.
So, what is a snippet? Well, they’re typically excerpts of text pulled from a particular article or page that contains content that Google thinks answers a user’s question. They’re then displayed prominently at the top of the search engine results page (SERP) in order to provide the user with a quick answer to their query.
You can easily tell if you’re looking at a featured snippet thanks to their prominent page positioning and the fact that their layout is reversed compared to other search results, having the content displayed above the site link instead of the other way around.
Featured snippets will also display the title and URL of the website providing the information, giving you a clear indication of where the information came from and how reputable the source might be. And if you’re lucky, they might even include an ‘also covered on this page’ section with links to other related headings within the content.
Regardless of their size and content, featured snippets are always displayed above other organic search results, often mixed in amongst the various paid ads Google points your way, and they’re more likely to appear when specific informational search queries are used as search terms.
What are the different types of featured snippets
Now that we’ve looked at the question “what is a snippet”, let’s touch on the different types of featured snippets you might come across. There are four distinct types of snippets:
- Paragraph or text snippets
- List snippets
- Table snippets
- Video snippets
The type of content that goes into forming a featured snippet will depend on the content present on the page. Text-based snippets tend to be picked first, followed by lists, tables, and then video snippets.
But it’s not just the type of snippet that can change, but its style of content as well. A text-based featured snippet might provide a very specific and concise answer in relation to a query or a briefer answer that is explained in full when you click on the snippet’s link.
A list snippet, on the other hand, could display an ordered or unordered list, depending on the list type, even hiding the top results of a list to get readers curious about what the top ranking results of a list are.
You’ll also usually get an image with your snippet, even if there’s no image on the site that accompanies it. Many snippets often contain a selection of collapsible arrow boxes containing further questions and snippets related to your query.
What is not a featured snippet
While it should be pretty clear now what a featured snippet is, it’s worth pointing out what things aren’t featured snippets, just so you don’t get confused when looking at the search results.
First, you shouldn’t confuse a featured snippet with a rich snippet. Rich snippets are designed to enhance organic search results and are results with different reviews attached to them in relation to the products and services that a site supplies.
Featured snippets should also not be confused with the knowledge panel that might be displayed on the right-hand side of a search results page or a knowledge card that can appear at the top of a page with basic information about a company or person.
Why should you target featured snippets
If it’s not obvious already, many good things can come from snapping up the featured snippet space at the top of a results page. After all, this top spot is sometimes called position zero and is exactly where you want to be when trying to rank your content on Google.
Right off the bat, you can expect to get a much better click-through rate (CTR) for any site that holds a featured snippet. Its prominent placement means users don’t need to scroll to find the info they want, making their life easier.
Stats also show that snippets get roughly 2x the CTR compared to non-snippeted content, making up 8% of all clicks online, showing them to be even better for a website than getting the number one position on a SERP.
And on top of all this, you get tons of exposure thanks to the amount of space it takes up above the page fold, boosting your overall credibility, visibility, and authority without needing to pay for a boost to be number one.
Now, while there is an argument to be made that CTR could drop with featured snippets because the snippet answers a user’s question, if a snippet is just a piece of the necessary information, users a far more likely to click on it. Basically, you can’t ignore featured snippets if you want to make the most of SEO ranking opportunities.
How to optimise for featured snippets
So, now that we know what snippets are, and why you need to make use of them, we need to talk about how to optimise for featured snippets. Optimising the content you want to be a featured snippet is a must, otherwise, Google will have no idea if you want the content to be a snippet at all.
Naturally, some content is more suited for snips than others, especially:
- Recipe content
- Best X content
- Vs content
- Make X content
- Definition content
But that’s not to say you can’t get a snippet if your content doesn’t fit into these categories. So long as the content in question is of good quality and correctly optimised, your odds of winning a featured snippet are high. Of course, there is no formula guaranteed to get you a featured snippet, but there are a few things you can do.
How to target featured snippets
One thing to bear in mind before you actually begin to optimise your own content to become snippets is whether or not you’ll be competing for the spot with your competitors.
This is easily done using analytical tools, like SEMrush and Ahrefs, which show what keywords have snippets and any gaps in the market that you can exploit. You can also do the same thing by Googling around your content and seeing what snippets come up.
Odds are you’re going to find some space in which you can target an available snippet. Even if it’s not your main point of content, just garnering a snippet will help all aspects of your site. If you spot some low-hanging fruit, you should absolutely go for it.
Now, it is also possible to target the featured snippets of competitors, especially if you think you can make better content than them. However, this is not an advisable strategy in the long run. Once someone has a snippet, it can be hard to unseat them from that spot, so it’s generally much easier to go for unclaimed snippets instead.
Featured snippet keywords
Right, first things first, when it comes to featured snippet optimisation, you must target the relevant feature snippet keywords or phrases associated with the content you want to form the snippet so that Google picks it up.
Get yourself some keyword tools and start researching, looking specifically for longtail, question-based keywords that users are likely to use when searching. Make sure you pick something with low keyword difficulty, and if you can, throw in a few trigger words; the words often used in queries like how to, which is, etc…
You also want to think about optimising the entire page content for keywords. Again, this indicates to Google that the page has good information related to a user’s query, encouraging it to rank the page higher. Either way, work your main keyword phrase into the snippet title and text, so Google picks up on it.
While not as important as they used to be, Google still uses keywords to help in its ranking calculations. To learn more about keywords be sure to read our blog on the best software to conduct keyword research.
Produce quality content
This is by far the biggest thing to bear in mind when it comes to optimising for featured snippets. You won’t get a snippet if the content you produce is of poor quality that doesn’t answer a user’s search query.
The content you make needs to be better than your competitor’s. That means good keyword density, solid internal and external linking structure, informative and well-researched information that meets the user’s needs, bulleted lists, and much more.
As a general rule of thumb, you want to include your keywords in the page title tag and any relevant headings, making sure to use headings in chronological size order for Google’s benefit and user readability.
With list snippets in particular, you want the keyword included in the list’s header, if possible, and followed by a succinct, bulleted list that gets the content across in a clear and concise manner.
You also want to stick to the recommended word count. Snippets tend not to be more than 40-250 characters or 40-50 words, depending on the featured snippet type. If you can, try to answer multiple related questions in one snippet, and should you have time, create a high-quality image to go with it.
Optimising content for SEO purposes is so important for any digital marketing strategy, so we highly recommend reading our beginner’s guide to writing SEO copy if you want to learn more about this topic.
Optimising your pages
Lastly, the other best practice you can follow to boost your odds of getting a featured snippet are the associated SEO qualities of the page. By boosting the ranking potential of your page, you automatically increase the odds of its content being picked for placement as a featured snippet.
Update your URL, get that metadata nice and tight, and make the page load times as short as possible. There’s a lot you can do to optimise a page. We suggest checking out our beginner’s guide on how to build backlinks for SEO, and our beginner’s guide on mobile-friendly SEO.
And that’s it! There’s not a whole lot more to say about featured snippets, but you should now have an understanding of their importance and how to start prepping your content to fit the featured snippet box. Remember, there’s no guarantee you’ll ever get a featured snippet, but if you do, it can be a game-changer.
As we’ve pointed out, featured snippets make up only a small part of the digital and organic marketing world. There are plenty of guides out there you can read to enhance your skills, including more like this one over on the c3 blog.
To find out more about us here at connective3, pop over to our website, where you can see examples of our work, the services we offer, and any available roles we have. Get in touch today to find out how we can help you take the next step in your digital journey.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Introduction
What do you think of when you hear the term search engine optimisation? Is it something tech-heavy and laborious? If it is, we don’t blame you. That’s certainly part of it, but if you’ve been reading our other guides on the topic of SEO, then you’ll know there’s a lot more to it than endlessly tweaking the code of a website.
You might also have guessed, especially based on the title of this article, that there is certainly a technical element to the way SEO functions. However, this shouldn’t put you off, because it’s not nearly as tricky as you might think once you’ve got a little bit of coding knowledge under your belt.
But we want to make sure you get off on the right foot when it comes to understanding what technical SEO is, and how to implement all the technical SEO tips we’re going to give you in this article. This might not be the most interesting stuff out there, but it’s absolutely crucial to know and implement.
If you’re ready to get started, let’s dive headfirst into technical SEO so we can get right to the technical SEO tips that will help you make any website rank better on the search engine results page (SERP)!
Points we’ll touch on
What is technical SEO?
Even with minimal exposure to SEO, you might already be aware that there are a few different types. These include:
- Off-site SEO, which relates to SEO away from your site.
- On-site or on-page SEO.
- Technical SEO, which is what we’re talking about today.
While off-site and on-site SEO can be rather nebulous in what they cover, technical SEO is very specific (though it does occasionally stray into on-site SEO territory).
From a top-down perspective, technical SEO is all about improving the internal structure of your website so that search engines can easily find, crawl, index, and render your site. This naturally involves a lot of technical work with regards to coding, ensuring your website is built in a language that search engines can understand.

Why is technical SEO important?
Technical SEO covers a myriad of behind-the-scenes elements, like site architecture, mobile optimisations, and page speed enhancements, all of which can go a long way in boosting your website’s ranking in the SERP.
But technical SEO isn’t just about getting better rankings. It’s about delivering a website that looks visually good to a user and search engine, is easily navigable, and is ultimately findable by search engines.
At the bottom level, you can have the best, most thoughtful content in the world on your site, but if Google can’t find the page to begin with, then the content is utterly irrelevant compared to fixing your site. If it can’t be crawled, it might as well not exist.
How to implement technical SEO
There’s a lot that goes into implementing technical SEO, that’s why we’ve created a nifty technical SEO checklist of things to do when you next have to optimise a website. That being said, however, there is one thing you should do before anything else with technical SEO, and that’s conducting one or more technical SEO audits.
Technical SEO audits
Even though the word audit might conjure up images of vast lengthy documents you need to trawl through, technical SEO audits are much simpler. Essentially, all a technical SEO audit does is assess the health of your website and tell you how to improve it.
This could include identifying broken links, orphaned pages, and suggested improvements for crawlability and indexing; the list is rather exhaustive. Google Search Console is a good auditing program to get started when it comes to tech audits as it’s completely free and easy to use.
Of course, if you’re building your website from scratch, auditing it is irrelevant as there’s nothing to audit, but it’s worth doing once you’ve built the website.
Our technical SEO checklist
With the audit out of the way, it’s now time to tick everything off on our technical SEO checklist. You might not be fully comfortable doing all of these as a beginner, but even addressing a few of the areas we’re about to discuss can massively affect the visibility of your website.
Streamlining your domain
One of the first things to look at with regard to technical SEO is to set up your preferred domain appearance. This governs whether or not you want a search engine to give preference to a www. or non-www. domain. All this initially does is dictate how your website will appear in search results. However, there’s another side to it.
You might prefer how one looks over the other, but more importantly, stating preference will ensure no search engine looks at both versions and assumes they’re different sites. Instead, it will redirect searches from your non-preferred domain to your preferred one, keeping everything nice and tidy when crawling and indexing.
Organising your website layout
Before we move on to discussing things relating to coding and site speed, we also need to touch on how a website should be laid out to maximise its crawlability.
As a general rule of thumb, your website should be built in a structure that makes it easy to find things, keeping pages linked together in a clear manner, and making page depth as shallow as possible.
Search engines rely on standardised website structures to make crawling as simple as possible. This is very important to getting your site indexed, which allows search engines to display them in the SERP. There’s a lot more that goes into crawling and indexing, all of which you can learn about in our beginner’s guide to how search engines work.
But, in short, you want to ensure that the main navigation features of your site are laid out in simple HTML code, alongside keeping the mobile and desktop versions the same with a focus on mobile display so search engine bots don’t have to crawl your site more than once.
And, of course, go through and make sure that the navigation on your site actually works. Check all your links go where they should, and ensure that there are no orphaned pages that could be missed in a crawl.
If you’re at all worried that your site could be missed for indexing, then registering with Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster means you can submit your website for indexing with a site map.
Site maps and schemas
Speaking of site maps, what are they and how do they work?
XML site maps are as they sound, they’re maps you can make to help search engines understand how to navigate your site. This comes in the form of a detailed site or page description, often including a page title, a description of its content, when it was last modified, how often it’s updated, the page’s priority, and any other elements on the page.
All this is put into the code of your website to make what’s known as a schema, which you can then submit to a search engine to assist them with their crawl and indexing. In essence, it will get your site indexed faster.
URL structure
If you’ve read our guide on on-page SEO, you’ll notice that we’ve already touched on URL structure. This is one of those areas where on-page and technical SEO blend into the same area but for different reasons.
While on-page SEO URL structure primarily focuses on how the anchor text of the URL relates to linking, technical SEO looks at how the URL appears in the search bar as a whole. Your URL gives search engines and users important information about the web page in question, and it should reflect what’s contained on the page.
For URLs, make sure they’re kept consistent in their structure, with logical categories and page information. Stick to using lowercase, separate words with a dash, keep them short and descriptive by cutting out unnecessary chaff, and if possible, include the keyword you want to target.
One other thing to note with your URLs is to ensure that every single one that makes up your website is HTTPS secure. You may have heard of SSL (Secure Socket Layer), but if you haven’t, don’t worry.
SSL is important for protecting users when they navigate the web. It creates an encrypted link between a server and a browser to keep any information entered by the user nice and secure from prying eyes. Google, in particular, is big on implementing SSL, so double-check all your pages have the little padlock by their URL.

Breadcrumb navigation
As you might have guessed by now, linking is a crucial part of technical SEO and site crawling in general. Besides making sure your internal and external linking structure is solid and functional, you also want to look at implementing breadcrumb navigation.
Breadcrumb navigation is a simple concept that allows users to easily return to the previous page they were on or right back to the homepage with a single click. It makes for an orderly site infrastructure as well as an additional layer of accessibility.
You can easily spot breadcrumb navigation on other sites by looking for the pathway bars at the top of pages, but you can also implement it with clear buttons back to the home page or the page they just came from.
Site and page speed
Other parts of on-page SEO that can blend with the technical side of things, site and page speed are super important when it comes to getting your site ranked properly in the SERP.
There are many ways you can speed up a site, including:
- Making use of fast hosting services.
- Keeping the number of HTTP requests your site needs to make to an absolute minimum.
- Cutting down on the number of site scripts and plugins used.
- Sticking to one CSS format.
- Shrinking or compressing your images to be as small as possible without causing them to pixilate.
- Compressing your website pages using tools like GZIP.
- Opting to use asynchronous loading so that all elements of a page can load simultaneously instead of one after the other.
- Tidying up the code of your site by removing unnecessary spaces, line breaks, indentations, and other excessive coding elements.
Site and page speed is also the perfect place to talk about site code and how it can impact your site’s loading.
There are three different types of coding language you’ll work with when it comes to websites:
- HTML – HyperText Markup Language provides the essential code structure for browsers to display your web content. It governs written content as well as headers, lists, body copy, alt text, etc…
- JavaScript – Java makes up the functional parts of a site, making dynamic elements function correctly and generally governing all the techy interactive stuff on screen.
- CSS – Cascading Style Sheets cover anything relating to the colours, fonts, and look of the site. Anything that makes it visually interesting.
There’s a lot of code that goes into making a site, hence why you want to keep it as minimal as possible with a focus on HTML. Java and CSS are more complex forms of code, and while they can make your site flashier, they can increase the render time of pages substantially.
All-in-all, the shorter you can make your page load times, the better.
User experience enhancements
Lastly, we come to improving the UX of your site. Again, we’ve covered some UX changes with on-site SEO, but there is still plenty you can do with technical SEO on this front.
First off, as we’ve mentioned, you want to focus on mobile indexing above all else, which means focusing primarily on making your site look good on mobile, with an emphasis on structure and user experience. Making use of Google’s accelerated mobile pages is a great option for this, being an open-source framework directed towards mobile sites.
On top of this, you want to eliminate any duplicate or thin content. Thin content gives search engines and users nothing to work with, often lacking internal links for crawling and failing to target user search intent. This needs to be bulked up or rewritten using on-site SEO knowledge.
As for duplicate content, besides eliminating it entirely (which we don’t always advise), you can merge pages together with redirects. However, if you’re an e-commerce site with multiple similar pages, making use of canonical tags can also be beneficial.
Canonical tags let you identify one page as the primary one that the search engine should focus on when crawling, preventing it from identifying the others as dupe content. Just be sure the canonical is relevant and not involved as part of a redirect.
Finally, be sure to eliminate or update dead links that go nowhere and include Hreflangs in your code to help with language changes under different IP addresses. You should also look to run through your site with an accessibility checker for those working with disabilities, all of which contribute to a higher ranking in the SERP.
While we’ve only covered the technical SEO tips you need to get started with technical SEO, you should be more than ready to get out there and start tweaking websites, so they jump higher up the SERP.
We do, of course, suggest going out there and getting more advanced training in all fields of SEO. But, if you found this guide useful, then we have plenty more available over on the c3 blog for you to read through. Why not take a look at our beginner’s guide to writing SEO copy or our beginner’s guide to mobile-friendly SEO?
You can also find out much more about what we do here at connective3 by looking at our work, roles, and service pages. Get in touch with our team today if you want to know more about what we can offer you in the world of digital marketing.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Introduction
Whether you’re just starting your career in the world of content and SEO, or you’re learning some new skills, blog writing is one of the best skills you can harness to help you in any sort of career. Being able to create engaging, informative content that doesn’t bore the reader and also manages to jump through the hoops of Google’s ‘Helpful Content’ update is no mean feat!
We’re here today to help you learn how to write a blog, covering the basics of SEO blog writing so you know that your content can rank, and also just how to create a good structure, how to create useful or entertaining content, and why all of this is hugely beneficial to your website.
Points we’ll touch on:
What is a blog?
Let’s start with a simple question – what is a blog? Well, blogs got their name from the term ‘weblog’ in the 1990s, which was the term for documenting your thoughts and lives on the World Wide Web. As blog tools for the internet became more accessible and easier to use, blogging really took off.
People used blogging as a personal diary, as a way to spread information about news and events, and even to document political or scientific discussions and findings. It was a way of getting the information and discussions that you found interesting out into the world where everyone else could see them. As of 2008, blogging had become so widely popular that a new blog was created every single second of every minute of every day that year.
Now the term blog has evolved and mutated into different strains since then – we’ve seen the stratospheric rise of vlogging, which is sharing your life, thoughts and findings via video recordings; we’ve seen the rise of food blogs, clothing blogs, book blogs; and now we see the adaptation of blogs by corporations too.
Companies and businesses can use blog forums that they host on their own website to share information, support, news, and helpful content with their customers. For example, a large department store may have a blog that details different ways you can use their products or a pet shop might have a blog about different products you can use to clean your pets. But why do they do this?

Why do blogs matter?
Blogs are really important for big and small businesses because they help elevate your brand and reach different types of audiences. By creating content that is insightful, entertaining, and useful to a website visitor, they are providing a helpful service, and are likely to either retain that customer or see that customer interact further with their site.
They might look at other blogs, click on some internal links to take them to a category or product page, and they may even complete a transaction if your blog (and product) were the answer to what they were looking for.
Do blogs help with SEO ranking?
If you want your business website to reach more people, or if you’re not completely satisfied with how highly you rank on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), then creating a blog can be a really big help. Blogs help to drive new traffic to your site that might otherwise not have known your brand before, especially if you use some key SEO tools, like great keywords.
Sowing keywords throughout your blog copy helps your blog pages to come up when people are searching for specific terms. For example, if you’re a flooring company, you might write a blog about how to remove stains from a carpet. By including keywords like ‘carpet stains’ and ‘how to get red wine out of the carpet’, your blog will hopefully show up on the first couple of results pages when people search for these terms.
Helpful and informative blog content can also help businesses rank higher when it’s created and structured well. Let’s take a more in-depth look at how you should do this.
How to structure a blog post
It’s always helpful to have a framework to work to when you’re creating brand new content – after all, a blank page can sometimes be a little intimidating!
Headings
By creating some headings, you can begin to create a structure and a narrative for how you’d like your blog to read. Headings are really important – the heading at the top of the page, what the blog is going to be called, is called an H1. You’ll only ever have one H1 on a blog post because this is the main title.
If you want to create different sections of content underneath this, it’s best to create subheadings for each section using H2s. If you want to create subsections within each section, then you’ll need to use H3s. It’s not advised to go as low as H4s – you might need to reconsider your structure if you’re getting as low as H4s!
If you’re struggling even to come up with different heading ideas, take a look at your keyword research (we’ve got a really handy blog if you want more information on how to conduct keyword research for SEO). This should be packed full of questions people want answers to and terms that they’re regularly searching for, and you should be able to formulate headings out of these and help you get a better idea of what you’ll be answering in each section.
Content
Now it’s time to let your creativity flow and get writing! Starting with the basics, you need a beginning, a middle and an end. So, this means including an introduction and a conclusion around the main chunk of your blog article, introducing the topic to your reader, and a recap at the end of the blog about what you’ve covered and where they can find more information.
Remember you’re telling a story to your readers every time you write a blog article – you want to take them on a journey from start to finish, constantly keeping them with you and ensuring that they’re not getting left behind. This is especially important if you’re explaining difficult or in-depth concepts, such as legal or financial procedures for example.
It’s really important when you’re writing any content that you keep a few things in mind:
- Your business’s tone of voice
- Your blog article’s purpose
- Word count
- Ways to keep the reader engaged with your website
- Your content should be helpful, entertaining and in no way misleading.
Google will penalise misleading content – so this means being careful not to promise that you’ll answer a specific query and not following through! You should aim to answer questions that users may have or provide them with information that they may be seeking. This is important to ensure that you don’t get penalties on your website, causing you to lose ranking positions and users.
Internal links
A great way to keep a user engaged with your website after they’ve finished reading your blog article is to insert links throughout the copy to other parts of your website. For example, if you’ve written that article on removing carpet stains, you might want to link through to your carpet page, or even your stain remover page. You could also link through to other helpful articles that are related, such as how to take care of your carpet, or the best type of carpet for family homes.
Not only is this helpful for your rankings and audience retention, but it’s also helpful for the reader. You might help them by answering other queries they may have had, and you might also lead them to products they may not have previously known about, or services that they hadn’t considered. Internal linking can also help you to bump up pages that you want more people to see, for example, a new carpet you’ve released, or a new cleaning service that you want to promote.
Multimedia
Including multimedia in your blog articles is another way of keeping the reader engaged, and it can boost your SEO rankings too. There are so many different types of multimedia you could include on the page to keep readers interested:
- Pictures
- GIFs
- Videos
- Graphs
- Page design
- Animation
- PDFs
- Downloadable attachments
- Audio
- YouTube clips
- Social media snippets
It’s a great way of engaging with your readers in different formats – after all, if you’re trying to explain something very complicated, or describe a route to take, or even want your reader to know what different steps of a recipe should look like, it’s important to have visual or audio cues there to help them.
You can use multimedia on your website to improve not only your user experience, but it can positively impact web crawler diagnostics, which are important metrics in SEO.
Metadata
When all of this is completed, your final step will be to write your metadata. We’ve got a really helpful article you can read if you want to know more about how to write metadata and why it’s important. This is another good place to get those keywords in, hopefully giving you a final bump in the SERP rankings. With that, you should be ready for proofing and publishing!
How to write a good blog post
So, you’ve got the structure, and the basic principles of writing a blog post, but what takes your blog post from basic to great? Well, aside from great writing, there are a couple of things you can do to improve the quality of your blogs:
Get your content proofed by someone else
We tend to skip over our own little mistakes when we’ve had our heads buried in a blog for a while, so getting a second pair of eyes on your work is key to making sure all the spelling and grammar mistakes are caught.
Research before you write a blog
There’s nothing worse than reading a blog that you can tell has been written by someone who has no clue about what they’re talking about. Becoming a bit more knowledgeable in the subject of your blog can only help and add to your blog content.
Hire a translator for translated work
Whatever you do, don’t use Google Translate! If you have work that needs to be translated from another language into English or vice versa, always use a skilled and competent translator, as you’ll appear unprofessional and an untrustworthy source in other countries otherwise.
Don’t be afraid to start again
If you find that you’ve spent all that time conducting keyword research, planning your blog, researching the topic endlessly, and when you sit down to write it, it turns out there’s not much to say, don’t worry about starting again. Your readers would much prefer to read content that is well-rounded, engaging, and informative than content for the sake of content.
Any content you can provide to your readers that’s helpful and insightful for them will be good, but you can make your content great with the tips in this article.
If you want to find out more about the different offerings that our content team can provide for your business, why not contact us or reach out on social media like Twitter or LinkedIn? For more help with SEO, content or even PR and Paid Media work, check out our blog which is packed with insights from our industry experts.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
In recent years, search engine optimisation (SEO) has become a fundamental building block for digital marketing.
Today, nearly all online businesses implement an SEO strategy to boost their online visibility, improve their search engine results page (SERP) rankings, and drive more organic traffic.
However, more recently mobile SEO is starting to take over. Given that approximately half of worldwide web traffic comes from mobile devices, mobile-friendly SEO is taking precedence over “normal” SEO. For a number of years now, Google has been emphasising the importance of mobile-first indexing – the use of the mobile version of content for indexing and ranking. More recently, though, the search engine introduced mobile-first indexing for the entire web!
An increasing number of online businesses and SEO professionals are shifting their focus towards the all-important domain of mobile optimisation. So, if your website isn’t mobile-friendly, it’s about time that you did something about it. Websites that still aren’t properly optimised for mobile SEO are inevitably wasting marketing efforts and losing much-needed sales.
In this beginner’s guide to mobile-friendly SEO, we’ll help you understand what SEO for mobile sites is, how it differs from normal SEO and how you can optimise your website for it. Let’s get started.
Points we’ll touch on:
What is mobile SEO?
Mobile SEO refers to improving the experience of visitors who navigate to your website from a mobile device, such as a tablet or smartphone. To do this, website owners must take steps to optimise their sites to make them more mobile-friendly.
In return, Google will reward such efforts with better rankings, visibility and, ultimately, more traffic to their sites.
Why is mobile SEO important in 2022?
We’re all aware that the world is becoming more and more mobile-centric by the day. So much so in fact, that, in 2022, the number of worldwide smartphone users is estimated at 6.6 billion – a 4.9% annual increase.
So, without a doubt, SEO for mobile sites is important to ensure all smartphone users have a great experience on your website. Mobile-friendly SEO ensures that your site presents your content in the best possible way for mobile searchers to understand.
If your website isn’t properly optimised for mobile SEO, you’ll almost certainly miss out on ranking improvements in the SERPs. To avoid this, you should do everything in your power to optimise SEO for your mobile site.
How is mobile SEO different to normal SEO?
If you haven’t shifted your focus to targeting mobile users, then it’s clear that you need to do so – and pretty sharpish. But what actually is the difference between mobile SEO and normal SEO?
How is mobile SEO different to normal SEO?
Mobile-first indexing was introduced by Google in 2018 and, as a result, search results for mobile and desktop are fairly similar – but definitely not the same. It’s crucial to understand the difference between desktop and mobile in search so that you have the best foundation upon which to build different strategies for desktop and mobile SEO.
The biggest difference between mobile and desktop search results is how text results appear in the SERPs. For example, mobile text results tend to be larger because Google places more emphasis on visuals when it comes to mobile. And, in many cases, images or videos will appear alongside mobile listings.
As such, only two to three mobile listings will fit on a screen at any one time, forcing mobile users to swipe multiple times to go through the results, taking longer to reach the bottom of the SERP. This means mobile users are more likely to click on the first few results rather than endlessly scrolling.
By contrast, up to five desktop listings can usually fit on a screen at once, making it easier for users to scroll through the results and get to the bottom much quicker. This suggests that it’s even more important to be at the top of the SERPs on mobile devices – otherwise, your listing might not even be seen.
Click-through rate
The second factor that tends to vary between desktop and mobile search is click-through rate (CTR). When you look at the CTR for mobile it drops less than that for desktop. On mobile, the CTR for the first-ranking position is 24%, compared to just 14% for the second-ranking position.
There are a number of potential reasons why CTR drops less for mobile than desktop:
- Mobile features individual cards for each listing, making it easier to look at individual listings
- Having photos on mobile listings further down the results page might be more visually appealing to mobile users
- The desktop’s wider screen means search results have more space to have multiple listings visible at a time, as well as sponsored ads and search features

How to optimise a website for mobile SEO?
Now we know how important it is to optimise your website for mobile-friendly SEO, how do you go about doing it? To improve your mobile SEO, there are some best practices you need to follow:
Improve your page speed
Any SEO knows how important page speed is to their efforts. The faster your web pages load, the better the user experience, and the better your search engine rankings will be. However, take that level of importance and multiply it by 10 for mobile SEO; because of hardware and connectivity issues, page speed is even more crucial for mobile users compared to desktop users.
Some ways you can improve your page speed include:
- Optimise images
- Minify code
- Reduce redirects
- Leverage browser caching
- Invest in better web hosting
Take advantage of structured data
Again, structured data is essential for any site, but especially for mobile site SEO. Structured data allows you to describe your website content in a way that search engines will understand. If your site is properly optimised using structured data, in return, search engines might reward you with rich results – enhanced results in the Google SERP with extra visual or interactive features, such as carousels and images.
Given that you have a smaller screen space on a mobile device, a search result with rich snippets is even more likely to stand out than on a desktop.
Optimise for local search
Users worldwide perform many “near me” searches on their mobile devices, for which Google returns more localised results compared to on desktops. Therefore, optimising your mobile site for local SEO is critical to gaining a competitive advantage in your industry.
There are a number of steps you can take to optimise your website for local search:
- Add schema markup to your site
- Update name, address, and phone number (NAP) citations
- Add your business to local directories
- Get reviews and add them to your site
- Identify local search terms and insert them into your content
- Claim your Google My Business Page
Responsive or dynamic?
Perhaps the most important decision you’ll make when it comes to mobile-friendly SEO optimisation is the type of mobile site configuration you use when setting up your site. You can choose between a dynamic serving or a responsive web design. Although Google tends to favour a responsive design, both options come with their pros and cons.
Responsive web design
The commonly recommended way of implementing a mobile-friendly website is the responsive web design setup. In this configuration, the web server sends the same HTML code to all users, irrespective of whether they’re using a desktop, tablet, or smartphone.
The code and content respond to each individual user, for example, adjusting to different screen sizes.
The main advantages of using a responsive web design setup include:
- Crawling of your website is more efficient, which improves the overall SEO of the site
- Your website loads quicker as there is no redirection for users on different devices
- Less chance of errors and mistakes resulting from poor device detection, URL redirection and displaying content, resulting in improved user experience
Dynamic web design
In the dynamic serving configuration, the URL remains the same for different devices, but the HTML/CSS file changes. This means that mobile and desktop users are presented with different content from the same URL.
The issue with this option is that device detection is dependent on a number of factors, some of which are often flawed and can lead to errors. As a result, it can cause the wrong versions of the web page to be displayed, ruining the user experience and sabotaging your mobile SEO efforts.
With this in mind, nowadays, most websites are configured using the responsive design setup. So, if you’re still using a dynamic web design, we’d recommend switching to improve your mobile-friendly SEO.
Seamless navigation
It should be super easy for visitors to explore your website, even if they’re searching on a mobile device. They should feel no difference whether they’re accessing your site on desktop, mobile or tablet.
For example, there should be adequate screen-tapping space for fingers. Two clickable elements should be separated by enough space to avoid confusion or incorrect clicking. Also, all buttons on your site menus must be neatly arranged, corresponding to the device screen size.
Don’t block CSS, Javascript or HTML
Blocking assets like CSS, Javascript, and HTML makes it more difficult for Google to access your site which could lead to a slip in rankings. You can check to see if you’re blocking any of these resources using your Google Search Console account.
Optimise titles and meta descriptions
It’s important to remember that you’re working with a lot less space when optimising mobile sites for SEO. So, to show off your best work in the SERPs, be as concise as possible when creating titles, URLs and meta descriptions.
How to check if your site is mobile-friendly
To check the mobile-friendliness of your site, either before or after you start optimising, you can use a variety of useful tools to gain useful insights. Some of the most effective include:
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
Using Google’s mobile-friendly test, you can either paste in your website’s URL or a specific code snippet, and Google will let you know whether the input is mobile-friendly or not.
If there are issues with your site’s mobile SEO, it will also highlight some of these, so you know which areas you need to focus on optimising.
Google’s Mobile Usability Tool
Another free tool from Google, the mobile usability tool can be found in your Google Search Console account.
Simply log into your GSC account and select “Mobile Usability”. If your website does have any errors, it will be shown under “Details”. The type of errors and the number of pages affected will also be shown.
Also, find out how to measure SEO success.
Conclusion
Mobile is the new normal – it is the baseline by which Google judges your website and assesses its suitability for search query rankings. So, if you’re trying to improve the visibility and ranking of your website, do NOT ignore the power of mobile SEO.
Do everything you can to fix the SEO for your mobile site and make it perfect, not just in Google’s eyes, but, more importantly, your visitors. After all, mobile SEO is not just about great content and a flawless technical profile but more about creating a killer user experience. By following our mobile SEO best practices, you’re sure to be on your way to the top!
Find out more about our SEO services and get in touch today. Or, to learn more about digital marketing, visit our blog.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Even if you’re new to SEO, you no doubt know just how much goes into building a solid SEO foundation for any website.
You need good content, a user-friendly interface, top keyword research, informative digital PR, and much, much more. All of which come together to make something Google wants to rank.
With all these vital pillars requiring a lot of careful time and consideration to grow and mould, the humble backlink might seem rather minor in comparison in relation to how something ranks in Google. But, as you’ll soon see, there’s much more to backlinks than simply offering a way for Google to reach a new site.
That being said, if you only have minimal SEO knowledge, you probably don’t know what a backlink is, never mind understanding why backlinks are important. Fortunately, backlinks are simple and easy to understand, despite their importance, as we’ll cover in this guide.
So, strap your SEO cap on and get a pen ready, we’re going to explain exactly what backlinks are, why backlinks are important for SEO, and how you can start link building today to get your content ranking on Google!
Points we’ll touch on:
What is backlinking in SEO?
In today’s constantly changing online world, the quality, relevance, and authenticity of online content is more important than ever. These three things are necessary for any content to rank, and they’re what make backlinks a viable and important strategy for driving organic content.
So, just what is a backlink?
Simply put, a backlink is where the URL for a particular piece of content or website is included as a hyperlink on a website that isn’t yours. As links are fundamental to navigating the web, this lets users find your content outside of your website thanks to a link that sends them back to you, hence the name backlink.
There are plenty of different types of backlinks out there that you can use, but in most cases, they’re created organically by journalists, influencers, bloggers, and anyone else who finds your content useful and interesting and wants to share it with others.
Making use of backlinks is necessary to compete in any industry with an online presence and have been a cornerstone of the Google algorithm since the 90s. And with that in mind, let’s take a closer look at how backlinks work in relation to SEO.
How does backlinking work?
If you’ve read our beginner’s guide to how search engines work, you’ll know that the primary way search engines find and store new information to be ranked is by crawling the web using links around and between websites.
Links take users to different pages, so by following the links on a page, Google can assess where a link goes, how good the information on this new page is, and whether or not it’s worth storing to be ranked in later search results.
But it’s not just content that Google considers when assessing pages. It also accounts for the number of links pointing to your page from other websites, if the sites providing the links are of good quality themselves, and if they give your page authority. All of these blend together to help you rank higher on the results page.
Essentially, backlinking means that Google isn’t just finding you through your own content, but from different sources, making it easier to find you, rank your content, and ultimately build your brand; and all it takes is a simple hyperlink from one caring soul on the internet.
How important are backlinks for SEO?
Now that you know what a backlink is, it’s time to turn to the question, “why is link building important for SEO?”.
Put bluntly, backlinks are one of the key ways you can drive that all-important search engine traffic to your site. Especially organic traffic. Without link building, it will take your content much longer to establish the kind of authority that makes Google want to rank it higher in search results.
Consistent and good-quality links show users that your content is valuable and worth their time, enhancing your brand and building trust between you and them. They show off your expertise and can eventually make you a leading figure in a particular niche or industry.
And, of course, they mean Google can crawl to your site from others, making you more prevalent in its crawls and getting your page indexed properly. In other words, an important page not being backlinked is hurting you more than you might think.
So, how important are backlinks? Very!
How to optimise a website for mobile SEO?
While gaining as many quality backlinks as possible is a big necessity for SEO, when it comes to actually getting links, the process is not as clear-cut as you might think.
In the past, it wasn’t uncommon for people to buy and trade links, or simply create a single page filled with links to your site, in a bid to fool Google into believing their content was of authoritative quality when it really wasn’t.
Nowadays, Google is far too smart to be fooled by such methods, either ignoring poor links or penalising your ranking for being over-optimised. Instead, to get links today, you need to focus on creating quality content that is relevant to users and worthy of being considered ranked by Google.
Usable link-building strategies
When it comes to getting links, more often than not, you’ll need to wait for them to build up naturally on their own or ask for links from those who might find your content interesting.
These two types of link-building strategies are known as passive and active link building, and we’re going to run through what they involve so you can start using them straight away in your work.
Passive link building
The first type of link building focuses on accruing links naturally over time. These are links that you don’t ask for and will usually make up the vast majority of links you gain. They tend to be generated over time thanks to good content that people want to share.
This content can be something you’ve created specifically for your brand or as a replacement for content that no longer exists, allowing you to solve the problem associated with broken links and displaying your content as the piece that Google wants to refer to most.
We’ve said it multiple times before, but we’re going to say it again one more time to knock it home. Creating and spreading good quality content is the number one way to get yourself noticed by Google, and like a symbiotic relationship, earns you backlinks.
For more info on how to create quality SEO content, be sure to read our beginner’s guide on writing SEO content.
Active link building
Active link building is much more direct, as the name suggests, and involves building relationships with other people in your industry, so you eventually get organic links. This means asking for links from people who would find your content interesting.
These links could be from journalists, bloggers, influencers, etc… who might be interested in your content and willing to link to it in their own work. Of course, your content must be deemed link-worthy to actually get links to begin with. This is the most direct way to get links and tends to be a key part of digital PR strategy.
Digital PR actually looks at combining passive and active link building together to create linkable assets for publications that might be interested in your content. This obviously has to be something relevant that publications want to link to, though, rather than something wholly irrelevant to them.
The content used in digital PR can be anything from a data-driven study to a detailed long-form guide, and the addition of good infographics or visuals alongside these never hurt either.
With a good piece of PR content directed toward those that’ll find it useful, people will want to cite it as a source, making it easier to ask them for links when they discuss the topic your content focuses on because they’re already interested in it.
Additional linking building strategies
Of course, you don’t have to only appeal directly to people when making new content. If you find previous content you’ve made being referenced elsewhere without a link, it never hurts to reach out and ask for a link to be put in seen as they’re already mentioning you.
You can even do this if you find people using your own image. Instead of asking them to take it down, you can ask them to link you instead, allowing you to benefit from their use.
Last, but by no means least, you can carry out something called link gap analysis, where you reach out to sites already citing your competitors and ask them to cite you as well.
You will, of course, need a good reason for them to cite you, but if they have linked to multiple different people in your industry already, then the odds of them linking you are high.
One other active link-building strategy you can pursue is outreach. This isn’t so much asking for links as promoting something someone else has already done by linking them from your website content. This puts you on their radar, and in theory, will result in you getting a link back.
This is a good strategy to employ when reaching out to influencers and can help you build long relationships for links in the future through mutual trust and good content. You get an advocate for your business through influencers, journalists, and writers, more of whom might contact you asking for your help in the future.
Ultimately, links tend to come naturally as a by-product of not trying to get links; it’s a bit of an oxymoron situation. But that doesn’t mean you can’t do more to speed the process along.
Things like good content, an exceptional PR campaign, or a new product launch are all designed to promote something else rather than gather links, which in turn actually generates backlinks.
Avoiding ‘toxic’ links
One very important thing to note when looking at backlinks is that not all links are as valuable as others. The only links you ever want to be associated with are those of good quality from reputable sites, not any link under the metaphorical sun.
Too many ‘toxic’ links will ultimately devalue your content in the eyes of Google, meaning it will rank you lower on the results page. This might seem unfair, as these links are outside of your control, which is why Google has implemented a method to get around them known as disavowing.
When you find sites that have links to your content but aren’t sites you want linking to you, you can use the Google Search Console to tell Google not to consider these links when ranking your page.
Backlinks are a prevalent and important part of SEO, one of which you hopefully now have a much greater understanding of. Of course, this is still a surface-level exploration of the topic, and there’s much more to learn about backlinks and their role in SEO, content, and digital PR.
And if you found this guide useful, be sure to check out some of the other guides here on the c3 blog, including our beginner’s guide to working in PR and our detailed article on what is content writing?
To learn even more about what we do here at c3, including the various services we offer and any current roles we have available, don’t forget to get in touch with our team. Together, we’ll help you start your digital agency journey or take your business to the next level.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
A dynamic media landscape and the rise of AI can prove difficult to manoeuvre, especially for brands or in-house teams without previous experience.
However, a changing media landscape does not necessarily change how campaigns are created.
Beginners need to know the foundations of PR campaigns to deliver great results consistently.
If you’re looking to create newsworthy concepts to build backlinks or raise further brand awareness for your business, this blog will look at the building blocks of digital PR campaigns to achieve great coverage and stellar backlinks.
Points we’ll touch on:
First things first – the brainstorm
The first step of any campaign is to find an original, but relevant idea. For this, you should come together as a team and throw ideas at each other, looking at what’s currently getting picked up in the media and how a story can stay true to your brand’s ethos and guidelines.
Key factors to consider for idea generation include your target audience’s interests and needs, vital media niches you want to reach with the campaign, what the competition is doing and whether you have the authority to comment on certain topics you’re thinking of exploring as part of the campaign.
For help on how to run brainstorms, you can read our helpful blog.
Once you have your idea it’s time to collate the data
Depending on your campaign, you might have to collect secondary data to back up your messaging. For example, if you’re a travel brand you might want to scope out the best areas for fine dining across the world. For this, you would need to source relevant data, such as restaurant reviews and accessibility. Untrustworthy data should be avoided at all costs, as this can harm your story and your reputation, too. If you’re using secondary data you must also ensure you have approval to use the data for media purposes too.
Some of our favourite data sources that we used to form campaigns include Statista, YouGov, ONS, FOI requests, consumer polls, social listening and general search trends.
You can also source experts within the field you’re covering to add further authority to your campaign including influencers and other experts depending on the topic you’re exploring. At connective3, to elevate our campaigns we often collaborate with influencers, professors and psychologists to name a few.
Supporting onsite content and designs
Once all data has been collated and triple-checked by you or the team, it’s time for design and copy. Now, not all campaigns require design and supporting onsite copy, especially if you’re planning to link to an already live section on your site such as a specific product page, but if you want to host content on your blog with supporting visuals, here are our tips.
Some examples of design you could use are:
- Infographics for tables or data
- Interactive pages to sit on-site
- Header designs for the on-site content
- Video design to accompany your blog
Content that sits onsite should also host more than just the data from your press release. Here, you can include more from your research or perhaps some supporting tips to make sure you’re offering journalists other link opportunities. Plus, this will allow you to jump on reactive stories in the future with the data you’ve gathered and hosted onsite.
Drafting your press release
While the content for the onsite blog and the design are being created, you can write the press release for your campaign. A crucial point of every release is to find the perfect hook that’ll catch the journalist’s attention immediately. It needs to be relevant, and newsworthy and cover important information including the who, what, why and when.
Building a media list
Relevancy is key when creating a media list and we always opt for quality over quantity. Your list should contain all relevant journalists to your story. You can find relevant journalists by using Google or other search engines by adding relevant keywords to see who has covered what in the past. Be sure to also look at your target publications and make sure the relevant journalists are also added to your list. Software such as Vuelio and Roxana can help you find relevant publications and journalists’ contact information.
The importance of an outreach plan, before outreach
Sometimes, your campaign can be ready to launch when suddenly breaking news erupts. Or perhaps you’ve launched your first angle and it’s just not bringing in the results you had hoped. So, first and foremost, you need to be prepared from the start. That’s why we always recommend having a thorough outreach plan in place. What angle are you launching first and why? Do you have different angles to approach different media niches with (you should)? What angles will you explore if the first doesn’t deliver? Or, if you’re aware of a potential situation that could impact the news agenda, do you have any supporting data or expert commentary from your campaign that can be elevated to use as a reactive opportunity should this happen? Always plan for the “what if”.
Building your results through media outreach
Once all your assets are live, you can start your outreach process. A tailored approach to relevant journalists is key. Look at what the journalists have written before and mention why you’re sending it their way. Do they cover wellness-led stories; Inform them your story fits their topics!
While no links can ever be guaranteed, there are ways you can increase the chances of coverage. At connective3, we look at what’s being covered in the news and adapt our subject lines and pitches to different journalists. Creating multiple angles to your story will also help you reach out to more journalists. However, don’t fall into the trap of bombarding journalists at once, you must take a tailored approach.
If you’re using software such as BuzzStream to help your outreach, look at the opening rates; is it low, or high? How many times do journalists open your emails, is it one, or perhaps five or six times? Reading the data from your initial outreach can help you adapt your press release for the future.
Hopefully, you now have a better understanding of what a digital PR campaign consists of. There are many key components and threads of information to keep track of, but with excellent time management and a strong team, you can create the most interesting digital PR campaign, and adapt it to the media landscape.
Want to learn more? Read more about the digital PR team and their work on our site.
Let’s get started
Want to know more? Contact us today to start achieving unprecedented results.
Are you looking to start a new career in Public Relations and wondering where to begin with figuring out what you want out of it, and potentially even what PR is?
We’ve put together this comprehensive guide to working in PR.
Starting with what the different forms of PR work are and what PR work looks like in c3, then taking a look at the different roles there are in PR, what tools PR teams use, and finally, how you can go about getting yourself a role in a PR team.
Points we’ll touch on:
What is PR work?
Public Relations, or PR, comes down to promoting a brand and protecting its reputation. You shape their outer image and push campaigns to the public that promote their tone of voice, their values, and their products. They push these campaigns through traditional and virtual media, like newspapers, radio, television, and social media, as well as blogs and vlogs.
PR uses these outlets as it allows brands to build relationships with their audiences and client base, as trusted news outlets tend to be viewed by the public as credible sources, giving your clients a trusted base on which to promote themselves.
Behind these campaigns goes a lot of work; research of trends, keywords, and strategy, as well as writing campaigns, pushing these out to carefully crafted lists of journalists and the members of the media industry, and then following up on these campaigns and monitoring them for results to present to your clients.
Public relations work can come in three forms – in-house, agency or freelance. In-house PR will involve working for one client and promoting their work, as well as working on the protective side of things too. Agency work, similar to freelance work, will involve working for multiple clients and managing multiple campaigns at once.
Agency work will see you working alongside a wider team of professionals, possibly data teams, social media teams and content teams to come up with your content, while freelancers likely have to balance multiple roles and responsibilities at once.
Whichever form of PR you fall under, there are a variety of roles that you could undertake, and different scales of progression that you could work towards.
What careers are there in PR?
There are different avenues you can follow within the umbrella category of PR roles – social media specific, traditional media-specific, content creation and management. We also have an international PR team that deals with clients across Europe and America, as we are lucky enough to have many team members who are multilingual, with team members who can speak German, Norwegian, Italian, and Spanish, to name a few, and you can find out more about this in the international section of our website.
Within c3, our digital PR team has a set structure of progression that goes:
PR Executive > Senior PR Executive > PR Strategist > Senior PR Strategist > Head of PR
Here’s a breakdown of each of those roles and their different responsibilities to give you a clear overview of what would be expected of you at each level.
PR Executive
Starting out, either as a graduate or as a new member of the PR community, you’ll likely start as a PR Executive or in a similar Junior PR role. The responsibilities for this role include:
- Building relationships with journalists and key media outlets across a variety of niches
- Time management, including the delivery of work to meet deadlines
- Press release writing
- Outreaching PR campaigns for backlinks
- Creative ideation for clients
- Collaboration with internal teams and client teams to improve results
- Maintain active social media profiles
Senior PR Executive
Stepping up to the next level is the Senior PR Executive role – this role has a lot of the same responsibilities as the junior role, but over time you’ll have honed your craft and will be able to interact more with clients and help to lead campaigns that you come up with. Our Senior Digital PR Executive position requires:
- Understanding of client’s challenges and competitor activity
- A deeper understanding of your client KPIs and overall account strategy
- Keeping up to date with the news and industry changes, including spotting proactive and reactive opportunities
- Helping to lead campaigns, including data and audience research/analysis
- Collaboration with internal teams and client teams to improve results
- Helping to train and support junior members of the team
PR Strategist
The step up from PR Executives to PR Strategists is significant – the role changes from a focus on writing campaigns to a focus on the strategy for your clients and more technical work involving creative strategy. The role includes responsibilities such as:
- Leading key client’s digital off-site strategies
- Planning budgets and resources for campaign activity
- Presenting strategies to clients and key stakeholders
- Understanding the client’s challenges and competitor activity
- Data and audience research
- Sourcing and briefing third parties, including designers and developers
- Building relationships with journalists and key media outlets across a variety of niches
Senior PR Strategist
There is another significant step up from PR Strategist to Senior PR Strategist – this involves running your own team of people and managing clients on your own. Alongside the usual responsibilities of campaign creation, you’ll also be expected to report on your campaign results and work much more closely with clients as a senior member of the PR team.
- Support the Head of PR
- Manage your team of PR Executives and Strategists
- Creation of client KPIs and account strategy
- Leading campaigns and providing full reports of results to your clients
- Helping to train and support junior members of the team
Head of PR
One of the top positions at c3 is the role of Head of PR. This role as the head of a department involves a lot more people management and spreading yourself over more campaigns in a supportive role rather than dedicating your time to one or two clients.
- Managing the PR team members
- Support all company campaigns
- New business research and finding new clients
- Managing team performance and KPIs
- Running your own accounts and clients
How does PR work?
We’ve got a lot of information in those job descriptions that might not make all that much sense – after all, to the uninitiated, what does campaign reporting or campaign ideation even mean? Here’s a breakdown of the process that our PR team go through with each of our clients:
Ideation
Coming up with campaign ideas is one of the most exciting and creative parts of PR work. This process normally involves a lot of collaboration both across the PR team and even other teams in your business to come up with ideas that will work for your current clients and potential future clients. Once you have a long list of ideas to work from, you can handpick the ideas that are most applicable and begin the research phase.
Data research/content creation
This part of the process is when you take your chosen idea and begin to find data to make your campaign interesting and newsworthy. This could involve reaching out to data collectors or even conducting your own research to get this data. Once you have all of the information you will need for your campaign, you can create your campaign assets, including any written or designed content. Now your campaign is ready to be sent out into the world!
Media outreach and research
Finding exactly the right publications and journalists who will be interested in your campaign is a really important step in this process – after all, if no one picks up your campaign then the results will be poor! Researching journalists and publications before you reach out will be invaluable, as you’ll make sure it lands in exactly the right inbox for it to take off. You will begin sending out your campaigns and keeping in touch with journalists to encourage them to share your campaign.
Report on and track campaign results
Once your campaign has gone out into the world, you’ll have to keep track of which publications share it, how many views it’s getting and whether the campaign has had any impact on your client’s business. Reporting these results back to the client (or your management team) is important, as it will let them know how well you’re doing.
Re-angling older campaigns
It’s important to remember that previous campaigns are never really finished – it’s always possible to revive an older campaign if it becomes newsworthy again, or if you can find a way to reangle it to make it work with current trends.
What tools do PR teams use?
To get great results on your PR campaigns and to ensure that the work process we’ve just gone through can go as smoothly as possible, we use a variety of online and downloadable tools. Here are some insights to help you get familiar with some of the different industry tools you’ll come across. There are several tools you can use depending on where you work, but most of them work in the same way.
We’ve separated them into three categories; campaign tools help you to manage and run campaigns, media tools help you to connect with journalists for the outreach of your campaigns, and SEO/trend tools help you to research different ideas for campaigns you could create in the future.
Campaign tools
With Buzzstream, you can launch and monitor outreach campaigns. The platform allows you to upload media lists, create and edit templates, and quickly send emails without having to manually send them one at a time.
You can manage and monitor influencer marketing campaigns using Hypeauditor, an AI-powered analytics and discovery tool. Additionally, you can use it to gather data and metrics about influencers across various social media platforms, including TikTok, Instagram, YouTube, Twitter, and Twitch.
Media tools
Among the best tools for reactive PR is ResponseSource, a sort of email subscription service that connects experts, PR professionals, and journalists. PRs can use this tool to send out their own requests for campaign support, such as expert commentary, besides responding to requests to promote their clients.
Using Vuelio is essential for building media lists and for outreach since it is essentially a public database of all sorts of media contacts from all over the world. You’ll especially benefit from this if you cannot find the journalist’s email on their website or in their Twitter bio.
SEO/Research tools
The Google Trends tool allows you to examine and analyse search trends over a period of time for a particular term or keyword. PR pros can use this as their source of data or boost the relevance of an existing piece.
Ahrefs, which is considered an all-in-one SEO toolkit, is a popular piece of software that we use across a variety of teams at C3. The tools available on Ahrefs include a site explorer, content explorer, keyword explorer, rank tracker, and link intersect.
With Keyword.io, you can find autocomplete keyword suggestions for popular search engines like Google, Amazon, and YouTube. There is no doubt that this tool is incredibly versatile, as it can be used by a variety of teams in digital marketing, including PR teams.
How to get into PR
While a degree in PR or media relations is a great way to prepare yourself for a role in PR and make yourself a great candidate for PR roles, it’s not the only way you can get into a role in PR! Here are some ways you can work towards a career in PR, and have some great examples to show in your CV when you do apply for any PR jobs:
- Keep up to date on news and trends – be aware of some of the big news items that are trending when you go for an interview/apply for a role. This is a great way to show that you have a finger on the pulse for trending topics and can come up with strong campaign ideas.
- Showcasing your writing capabilities e.g., start a blog, freelance for some magazines/newspapers/student journals – strong writing abilities are key for working in PR.
- Demonstrate initiative – being able to show that you can step up when a member of your team is incapacitated will stand you in good stead to step up to help on campaigns that need extra help.
- Showcase your creativity – whether you love creative hobbies or can showcase any creative projects you’ve been a part of, you’ll show any prospective employers that you can think outside the box and create unique ideas.
A career in PR is a great starting point for creative people with a vision to create projects that they want to shout about loud and proud – if you think that PR could be the right career for you, start working on your progression today!
For more information on what it’s like working in PR, make sure you check out our PR starter pack.
If you’d like to speak to any of our PR team about anything we’ve covered in our guide, you can get in touch with us to chat some more. You can also find all of the roles that we are currently looking for in the careers section of our website.
Let’s get started
